Customer personalization has become the cornerstone of modern marketing. Businesses that understand their customers’ behavior, preferences, and needs can deliver highly relevant experiences, which in turn boost customer satisfaction, loyalty, and sales.
But personalization requires more than just guesswork; it demands the effective use of customer data.
In this guide, Brandout Adv explains how to utilize customer data for personalization, covering the types of data to collect, ethical considerations, tools available, and practical tactics for implementing personalized campaigns.
Why Customer Data Matters for Personalization
Customer data provides a detailed view of who your customers are and what they want. Without data, personalization becomes a guessing game. When used properly, customer data allows businesses to:
- Understand customer demographics and behavior.
- Segment audiences based on preferences.
- Deliver timely and relevant offers.
- Improve the customer experience.
- Build long-term relationships.
Types of Customer Data
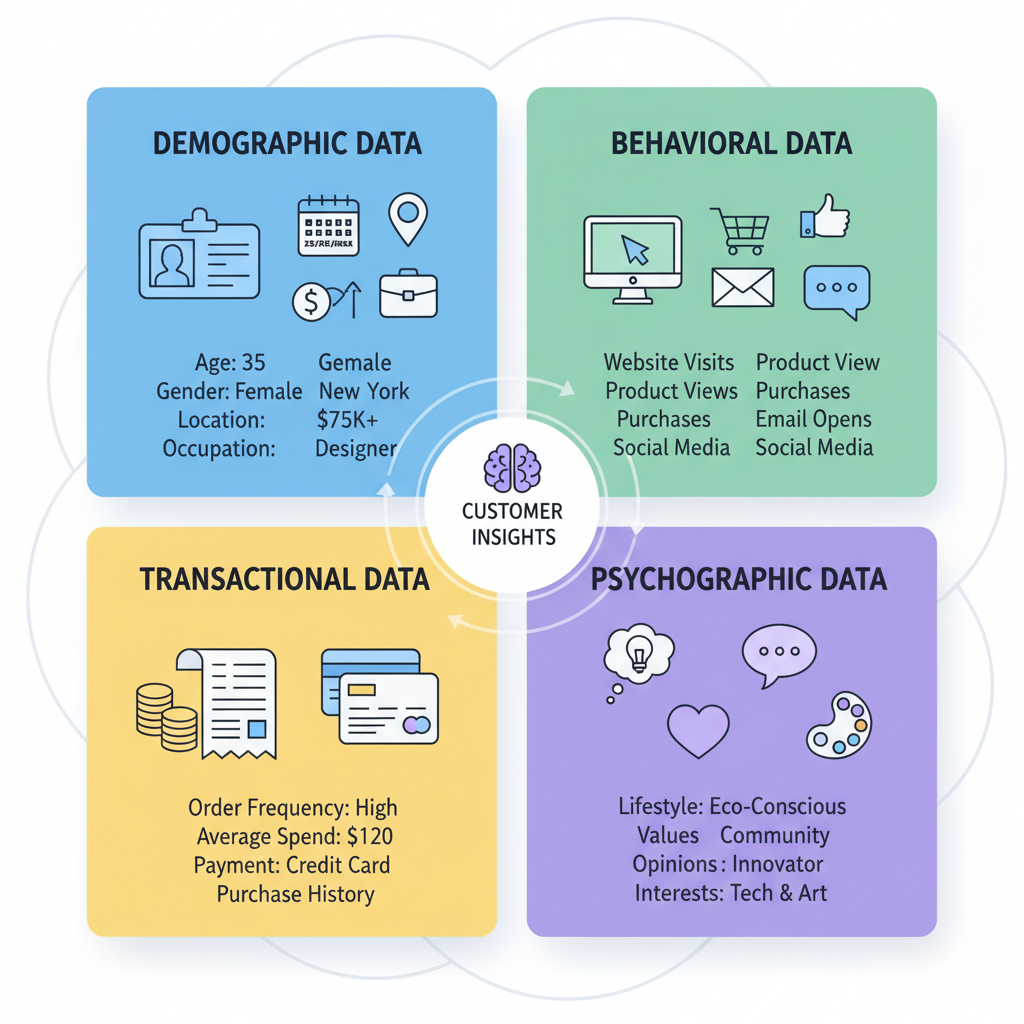
Customer data can be broadly categorized into four types:
Demographic Data
Includes basic information such as age, gender, location, income level, and occupation. This data helps you segment customers into groups and design campaigns accordingly.
Behavioral Data
Covers how customers interact with your brand: website visits, product views, purchases, email opens, social media interactions, and more. Behavioral data reveals interests and intent.
Transactional Data
Contains information about customers’ purchase history, such as order frequency, average spend, and preferred payment methods. This is crucial for loyalty programs and upselling opportunities.
Psychographic Data
Involves customers’ lifestyles, values, opinions, and interests. Psychographic data allows you to create emotional connections and targeted messaging.
How to Collect Customer Data Responsibly
Collecting data should always be transparent, ethical, and compliant with regulations such as GDPR or local data protection laws. Here are some best practices:
Obtain explicit consent from customers when collecting personal data
When requesting customer data, always provide a clear and visible option for them to opt in rather than assuming consent actively. Use checkboxes, double opt-in emails, or confirmation pages to ensure they genuinely agree. This practice complies with privacy regulations and strengthens trust. Customers who willingly share their data are far more likely to respond positively to future personalized campaigns, resulting in better engagement and higher retention rates.
Explain how the data will be used to improve their experience
Transparency is crucial. Clearly outline, in simple language, how you will use the data customers provide. For example, state that their information will help you offer more relevant promotions, recommend products they like, or improve your services. Avoid legal jargon or vague statements. When customers understand how they directly benefit, they feel respected and are more likely to continue sharing their information with your business over time.
Allow customers to opt out at any time
Give customers total control over their personal data by making it easy to unsubscribe, change preferences, or withdraw consent. Place visible “unsubscribe” links in emails, provide a dedicated preferences center, or let them contact support to opt out quickly. This approach not only meets legal requirements but also reinforces your commitment to respecting privacy, which strengthens your brand’s reputation and encourages trust-based long-term relationships with your audience.
Store and process data securely to protect privacy
Protecting customer data is non-negotiable. Use encrypted servers, secure data centers, and strict access controls to prevent unauthorized access or leaks. Regularly update security protocols, run vulnerability audits, and comply with recognized standards. Demonstrating that you handle information safely reassures customers and encourages them to provide accurate data. Secure storage practices also reduce the risk of fines or damage to your reputation, ensuring long-term operational stability.
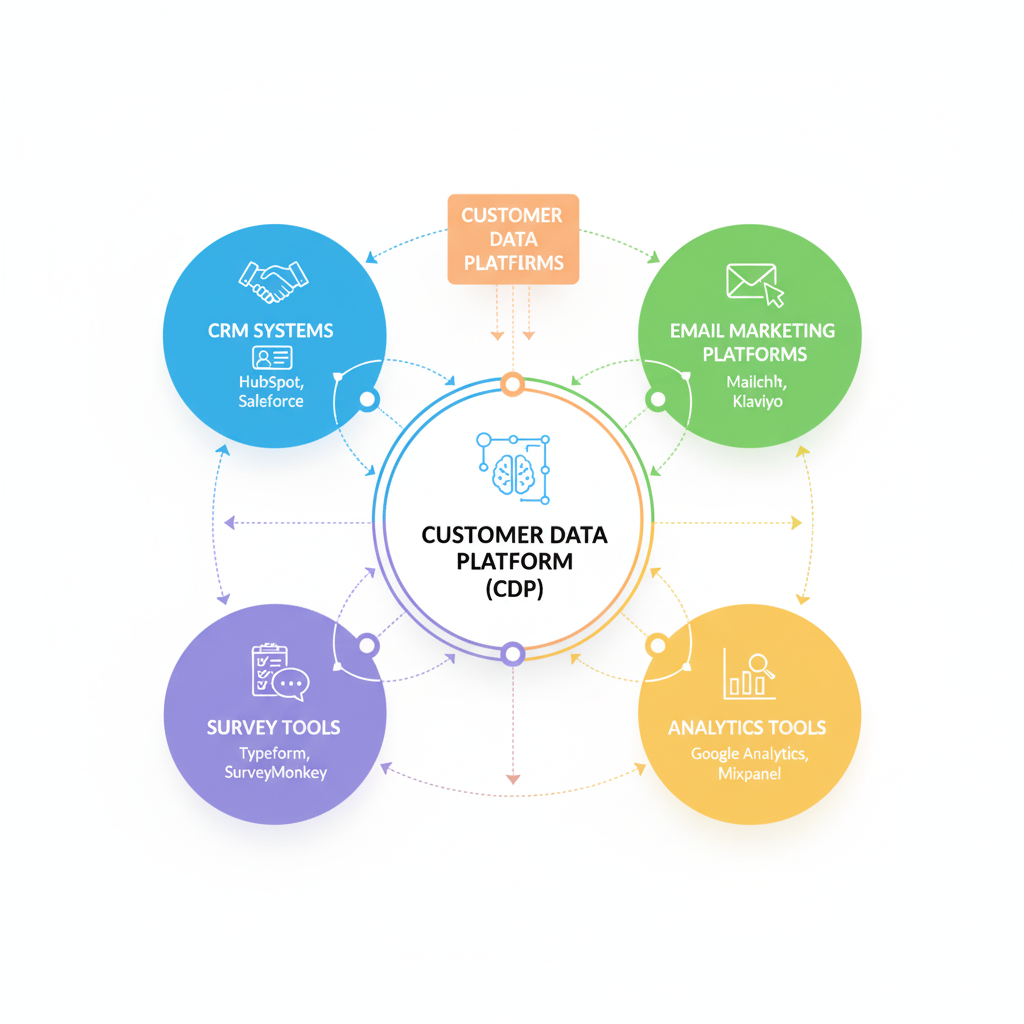
Tools for Collecting and Managing Customer Data
Several tools can help businesses gather and organize customer data effectively:
- CRM Systems (like HubSpot, Salesforce): Store customer information, track interactions, and manage relationships.
- Email Marketing Platforms (like Mailchimp, Klaviyo): Track opens, clicks, and customer engagement.
- Analytics Tools (like Google Analytics, Mixpanel): Analyze website behavior and traffic sources.
- Survey Tools (like Typeform, SurveyMonkey): Collect feedback and psychographic data.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) (like Segment, Bloomreach): Combine data from multiple sources into a single customer profile.
Segmentation: Turning Data into Actionable Groups
Segmentation is the process of dividing your customers into groups with similar characteristics or behaviors. Effective segmentation allows for targeted messaging and offers. Examples include:
- New vs. returning customers.
- High-value vs. low-value customers.
- Geographic location segments.
- Engagement level (active, dormant, churn-risk).
Personalization Strategies Using Customer Data
Once your data is organized, you can apply it to create personalized experiences. Below are actionable strategies:
Personalized Email Campaigns
Use customer names, purchase history, and browsing behavior to send highly relevant emails. Examples:
- Product recommendations based on previous purchases.
- Reminders about abandoned carts.
- Exclusive offers for loyal customers.
Dynamic Website Content
Show different website content based on the visitor’s data. For instance, a returning customer might see recommended products or loyalty rewards, while a first-time visitor sees a welcome offer.
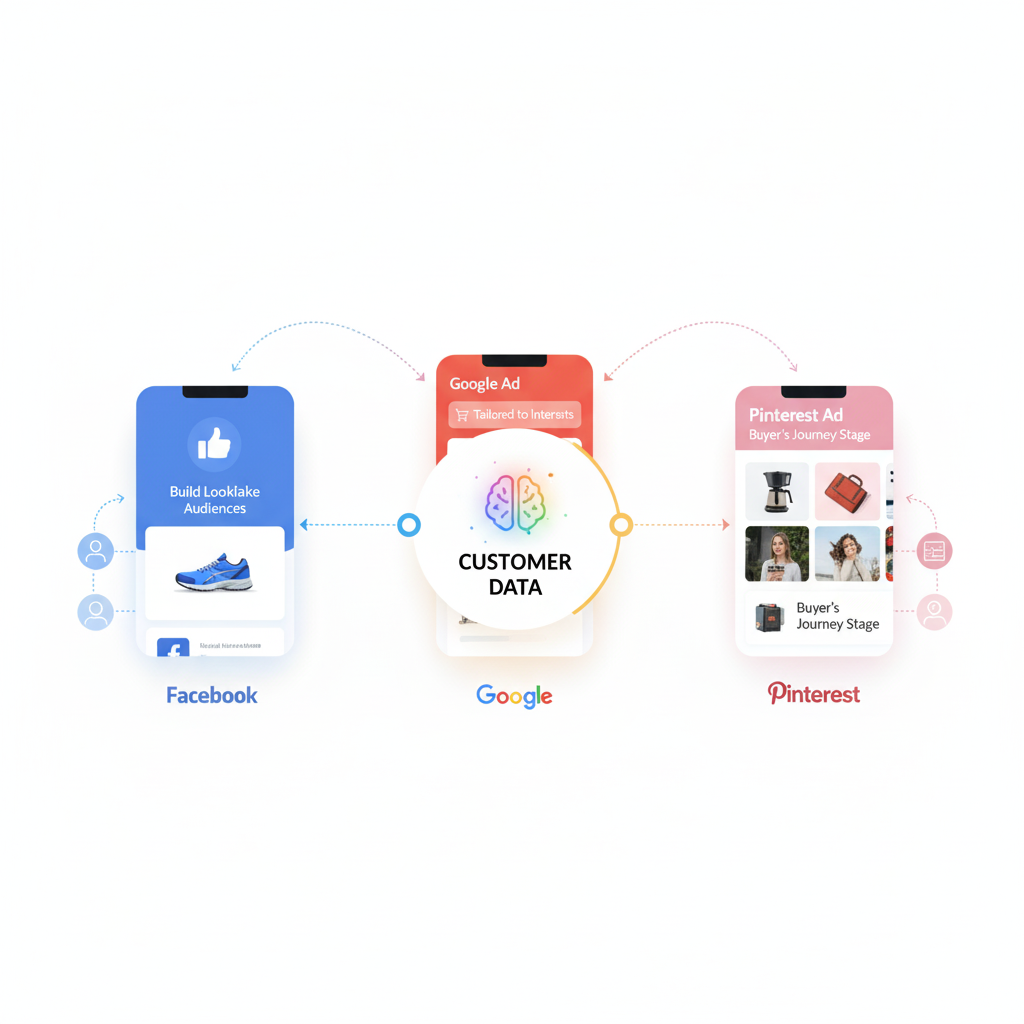
Targeted Ads
Leverage customer data to build lookalike or custom audiences on platforms like Facebook, Google, or Pinterest. Deliver ads tailored to customer interests and stage in the buyer’s journey.
Loyalty Programs
Use transactional data to reward frequent customers with discounts or points. Personalize offers based on spending habits.
Product Recommendations
Integrate recommendation engines (like Amazon does) to suggest products that customers are likely to buy based on past behavior and preferences.
Personalized Customer Support
Equip your support team with customer history to provide faster, more tailored assistance. Chatbots can also greet returning users by name and recall past issues.
Measuring the Success of Personalization
You must track performance to ensure your personalization efforts are working. Key metrics include:
- Conversion rate.
- Average order value.
- Customer lifetime value.
- Email open and click-through rates.
- Customer satisfaction and Net Promoter Score (NPS).
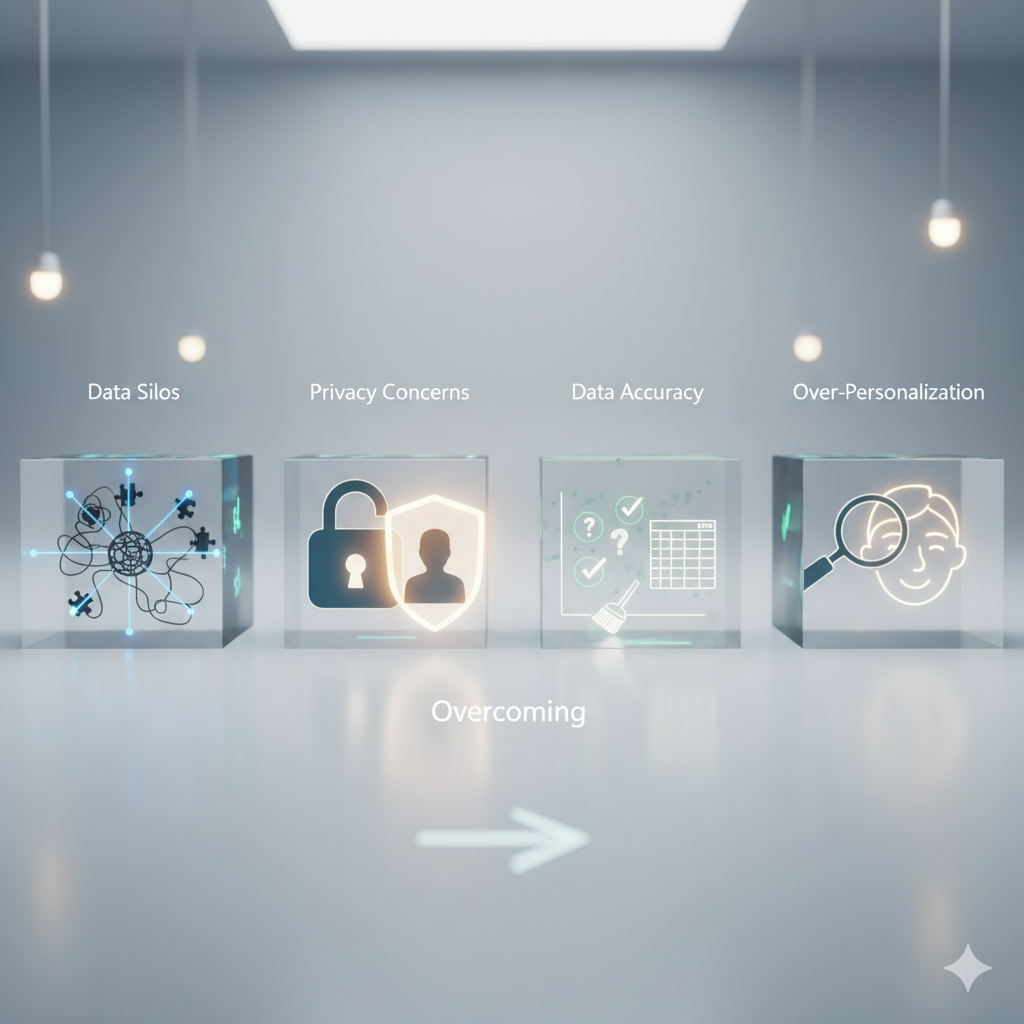
Overcoming Common Challenges
While personalization has clear benefits, there are challenges to manage:
- Data Silos: Customer data is spread across different platforms. Solve with integration tools or CDPs.
- Privacy Concerns: Customers may be wary of sharing data. Build trust with transparency.
- Data Accuracy: Incomplete or outdated data reduces effectiveness. Regularly clean and update your database.
- Over-Personalization: Too much personalization can feel invasive. Strike a balance.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Always ensure compliance with data protection laws. Respect customers’ privacy and avoid using sensitive data inappropriately. Following ethical practices builds long-term trust and brand reputation.
Advanced Personalization Tactics
For brands looking to go beyond basics, consider:
- Predictive Analytics: Use AI and machine learning to predict future customer behavior.
- Real-Time Personalization: Deliver messages instantly as customers interact with your brand.
- Omnichannel Personalization: Provide a seamless experience across email, website, mobile apps, and in-store.
- Behavioral Triggers: Automate responses based on customer actions, like sending a thank-you email after a purchase.
Examples of Successful Personalization
- E-commerce Store: Uses browsing and purchase data to recommend products and send personalized discount codes.
- SaaS Company: Segments users by usage patterns and sends targeted onboarding emails to improve retention.
- Local Business: Sends personalized SMS reminders for appointments based on previous visit history.
Steps to Implement Customer Personalization with Brandout Adv
- Audit Current Data: Identify what data you already have and where it resides.
- Choose Tools: Select CRM, email platforms, and analytics tools suited to your needs.
- Segment Your Audience: Group customers based on demographics, behavior, or value.
- Create Personalized Campaigns: Develop email sequences, ads, or website content tailored to each segment.
- Test and Measure: Use A/B testing to refine your personalization efforts and monitor key metrics.
- Scale and Automate: As your personalization strategy matures, automate processes to handle larger customer bases efficiently.
Future of Customer Personalization
Personalization will continue to evolve with AI, predictive modeling, and more sophisticated data collection methods. Businesses that invest in personalization today will stay ahead of competitors and meet rising customer expectations.
Conclusion
Using customer data for personalization is no longer optional — it’s essential for building strong relationships, increasing revenue, and staying competitive. With a responsible approach to data collection, effective segmentation, and thoughtful execution, businesses can create experiences that delight customers and drive long-term growth.
Brandout Adv helps businesses implement customer data-driven personalization strategies, from data collection to campaign execution, ensuring your brand connects meaningfully with every customer.
Most Asked Questions
Here are 4 fresh FAQs not already covered in the text above:
How can small businesses collect customer data without expensive tools?
Small businesses can start with free or low-cost options like Google Forms for surveys, built-in analytics on social media pages, and free CRM tiers. Even spreadsheets combined with email marketing platforms can help organize basic customer information before scaling up to paid tools.
What kind of data should never be collected for personalization?
Avoid collecting highly sensitive information such as national ID numbers, financial credentials, or health details unless essential and legally justified. Sticking to non-sensitive demographic, behavioral, and transactional data reduces risk and improves customer trust.
How often should businesses update and clean their customer data?
Customer data should be audited and cleaned at least once every quarter. Removing duplicates, correcting outdated records, and verifying email addresses improves personalization accuracy and prevent wasted marketing efforts.
Can personalization be effective without collecting personal names or emails?
Yes. Even anonymous data such as browsing behavior, device type, or location can be used for personalization. For example, showing region-specific offers or recommending products based on on-site activity works without needing personally identifiable information.