Drupal has long been known as one of the most powerful content management systems, trusted by enterprises, governments, and developers around the world. Its flexibility and scalability make it an excellent choice for building complex websites.
But as digital experiences continue to evolve across devices and platforms, traditional CMS setups are sometimes too limited. That’s where the concept of a Headless CMS comes in, and Drupal fits that role remarkably well.
Choosing Drupal as a Headless CMS allows businesses to separate content management from content presentation, creating faster, more dynamic digital experiences. Instead of being confined to a single website theme, your content can power mobile apps, IoT devices, and multiple front-end platforms from one central hub.
This guide explores everything you need to know about using Drupal as a Headless CMS, from what it means, how it works, its key advantages, and where it fits into your digital strategy.
What is a Headless CMS?
A Headless CMS is a content management system that manages and stores content without being tied to a specific front-end design. In a traditional CMS, the “head” refers to the presentation layer, the theme, templates, and user interface.
When a CMS is “headless,” it means this presentation layer is removed or decoupled, leaving only the backend where content is created, organized, and distributed.
This content can then be delivered to any platform or device through APIs. Whether you’re building a mobile app, an interactive website, or a smart display, the Headless CMS acts as a centralized content source.
In simple terms, instead of one system controlling both content and visuals, a Headless CMS focuses purely on content delivery. The front-end developers can use modern JavaScript frameworks like React, Vue, Angular, or even mobile frameworks like Flutter to create unique, fast, and user-friendly interfaces.
For businesses, this means:
- More flexibility in how content is displayed and reused.
- Faster performance since front-end and back-end are independent.
- Easier integration with multiple digital channels.

Understanding Drupal as a Headless CMS
Drupal, by design, is already modular and API-friendly. Its architecture makes it easy to use as a traditional CMS or as a Headless CMS, depending on the project’s needs. When you use Drupal in a headless or decoupled setup, you are essentially letting Drupal handle all the content management while another system or framework handles how that content is displayed to users.
Drupal becomes the content engine, storing everything from blog posts and product data to multimedia and structured fields. Instead of rendering templates, Drupal sends this data through RESTful APIs, JSON:API, or GraphQL, which front-end applications can consume and present however they want.
This flexibility allows developers and businesses to use Drupal’s strong backend capabilities while taking advantage of modern front-end technologies. For example, a company can manage its blog, eCommerce catalog, and app content from Drupal, while delivering it to a React-based website and a mobile app at the same time.
What makes Headless Drupal especially appealing is that you don’t lose any of the powerful tools Drupal is known for, such as:
- Robust user roles and permissions
- Multilingual support
- Advanced taxonomy and content structuring
- Editorial workflows and content moderation
You can think of Drupal as a highly intelligent content service that powers multiple digital experiences simultaneously.
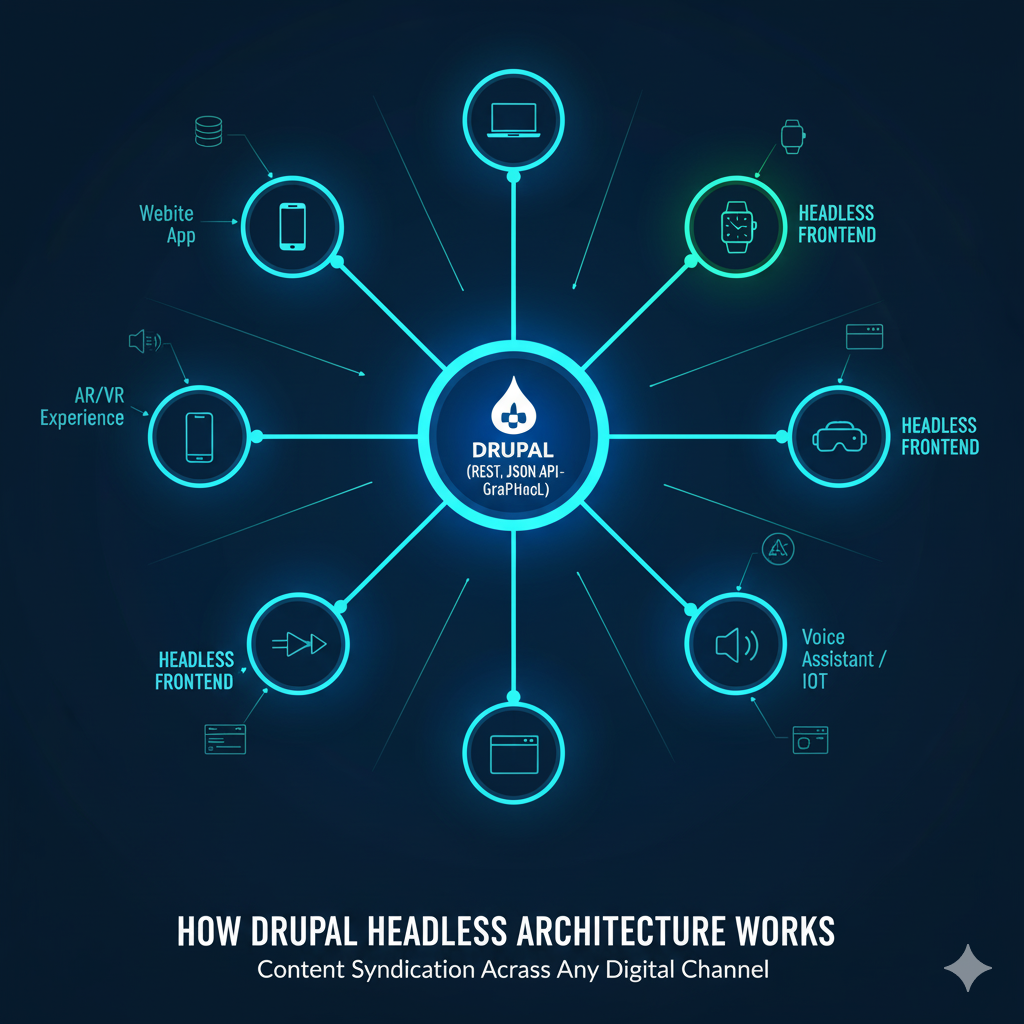
How Drupal Headless Architecture Works
To understand how Drupal as a Headless CMS functions, think of it as two main components working together: the backend (Drupal) and the front-end (your chosen framework).
Drupal manages all your content, pages, images, product data, and metadata. The front-end, built with JavaScript frameworks such as React, Vue.js, or Angular, handles how users see and interact with that content. Communication between these two layers happens through APIs.
When a user visits your website or app, the front-end sends a request to Drupal’s API asking for specific data, such as an article, image, or menu. Drupal retrieves this data from its database, packages it into a JSON response, and sends it back to the front-end. The front-end then displays that data in the user interface.
This process may sound technical, but the concept is simple: Drupal is the content warehouse, and your front-end is the shop display. You can redesign the display anytime without touching how the content is managed.
Drupal offers several API options to make this possible:
- RESTful Web Services – The standard option for exposing content and data structures through REST endpoints.
- JSON:API – A more modern and standardized way to deliver structured data in JSON format, ideal for most headless projects.
- GraphQL – A flexible query language that allows front-end developers to request exactly the data they need, reducing unnecessary load times.
The result is a smooth and scalable architecture that lets teams work independently. Content creators manage and update content in Drupal without worrying about design or code, while developers build and optimize front-end experiences freely using the latest technologies.
This decoupled structure is especially valuable for large businesses that need to deliver content consistently across multiple platforms like websites, apps, smart TVs, or digital kiosks.
Key Benefits of Using Drupal as a Headless CMS
Choosing Drupal for a headless setup offers several business and technical advantages. Whether you run an eCommerce store, a news portal, or an enterprise website, this approach can significantly improve performance, flexibility, and scalability.
Unmatched Flexibility
One of the biggest reasons companies choose Headless Drupal is flexibility. Developers aren’t restricted to Drupal’s theming system, so they can design unique interfaces using any technology. Marketing teams can still manage content within Drupal, and that content can appear on multiple channels.
This setup ensures faster innovation since front-end and back-end updates don’t interfere with each other.
Better Performance
A decoupled front-end usually loads faster because it can use modern JavaScript frameworks optimized for performance. By offloading the presentation layer, Drupal can focus solely on managing and serving data efficiently. The result is smoother user experiences, shorter load times, and better Core Web Vitals scores.
Future-Proof Technology
The web evolves quickly, and design trends change every few years. With Drupal as a Headless CMS, you’re not locked into a single front-end technology. If a new framework becomes popular or your business wants to launch a new digital product, you can keep the same Drupal backend and build new front-ends with ease.
Omnichannel Content Delivery
Businesses today reach audiences through websites, mobile apps, social media, and even devices like voice assistants or smart displays. A Headless CMS allows you to deliver consistent content to all these channels from one source.
For instance, a product description managed in Drupal can automatically appear on your web store, mobile app, and catalog kiosk, no duplication required.
Easier Maintenance and Team Collaboration
By separating the front-end and back-end, development teams can work simultaneously without conflicts. Back-end developers focus on data and structure, while front-end teams handle design and interactivity. This makes development cycles shorter and maintenance easier.
Common Use Cases for Headless Drupal
Drupal’s flexibility and scalability make it suitable for a wide range of digital projects. Here are some practical scenarios where Drupal as a Headless CMS truly shines:
Multi-Channel Content Platforms
If your business manages content across different platforms, like websites, mobile apps, and digital signage, Drupal can serve as the central hub. This ensures content consistency and reduces manual updates.
E-commerce Experiences
E-commerce brands can use Drupal to manage products, categories, and marketing content, while frameworks like React or Next.js handle the storefront. This creates lightning-fast, customizable shopping experiences without losing Drupal’s strong backend features.
Corporate Websites and Portals
Large organizations often have complex content needs, news updates, internal portals, and regional websites. A headless setup lets them distribute the same content globally while maintaining different designs or languages per region.
Mobile Applications
Many mobile apps now rely on headless architectures to fetch data dynamically. Drupal’s robust API support makes it perfect for powering mobile content, user data, or notifications.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs combine the feel of mobile apps with the reach of the web. When powered by Drupal’s APIs, PWAs can display fresh content instantly, even offline, providing users with a fast and engaging experience.
Front-end Frameworks Compatible with Headless Drupal
One of the greatest strengths of using Drupal as a Headless CMS is the freedom to choose any front-end technology. Since Drupal delivers content through APIs, it can connect to nearly any framework or platform that can consume data in JSON or GraphQL format.
Let’s explore some popular options and why they pair well with Drupal.
React.js
React is one of the most widely used JavaScript libraries for building fast and dynamic user interfaces. When combined with Drupal, React can fetch data from Drupal’s JSON:API endpoints and render it efficiently in real time. This makes it ideal for interactive applications, dashboards, or single-page websites that require smooth transitions and modern user experiences.
React also supports frameworks like Next.js, which adds server-side rendering and SEO optimization, making it a top choice for headless Drupal websites.
Vue.js
Vue.js is lightweight, easy to learn, and offers flexible integration. Many developers prefer Vue for projects where quick development and simple integration are priorities. Drupal’s data can be consumed directly into Vue components, allowing teams to build engaging interfaces without complex setup.
Vue also has strong community support and can scale from small projects to enterprise-level applications.
Angular
Angular is a comprehensive front-end framework maintained by Google. It’s ideal for large-scale, data-driven applications with structured architecture. When used with Drupal, Angular can manage content dynamically, synchronize updates, and handle complex user interactions.
Although Angular has a steeper learning curve, its robust ecosystem makes it suitable for enterprises with long-term development plans.
Gatsby
Gatsby is a React-based framework focused on performance and static site generation. It works perfectly with Drupal as a data source, fetching content during build time and serving static pages that load instantly.
This setup is ideal for blogs, marketing websites, and documentation portals that prioritize SEO and speed. Drupal’s editorial flexibility combined with Gatsby’s front-end optimization creates a strong balance between power and performance.
Flutter and Mobile Frameworks
For mobile apps, frameworks like Flutter or React Native can use Drupal as a content backend. This lets you reuse the same content from your website for your iOS and Android apps, ensuring a unified brand experience across devices.
How to Set Up Drupal as a Headless CMS (Overview)
Setting up Drupal as a headless CMS may sound complex, but at its core, it involves a few straightforward steps. Here’s a beginner-friendly overview of how it typically works:
Step 1: Install and Configure Drupal
Start by setting up a standard Drupal installation. Choose the latest stable version (Drupal 10 or above) for better performance and built-in API features. Configure your content types, taxonomies, and fields according to your project needs.
Step 2: Enable API Modules
To expose your content to external applications, enable one or more of Drupal’s API modules. The most common options are:
- JSON:API – Recommended for most projects, it provides ready-to-use endpoints for all your content types.
- RESTful Web Services – Offers customizable endpoints but requires more manual configuration.
- GraphQL Module – Provides a query-based API, letting developers fetch exactly the data they need.
Once enabled, your content is instantly available as structured data through specific URLs.
Step 3: Build the Front-End Application
With APIs ready, developers can start building the front-end using frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular. They’ll fetch data from Drupal’s API endpoints and render it dynamically.
During this process, developers can also implement routing, caching, and performance optimizations on the front-end side.
Step 4: Connect and Test
The front-end and back-end communicate through HTTP requests. It’s important to test these connections to ensure data flows correctly between the systems. For example, fetching an article or product list from Drupal should display accurately on your front-end interface.
Step 5: Deploy and Scale
Once everything is tested and stable, both layers can be deployed independently. You can host Drupal on a secure backend server or cloud platform and host your front-end application on a CDN for faster global performance.
This separation also means scaling is easier, you can upgrade your front-end or back-end without affecting the other.
Challenges and Considerations
While Headless Drupal offers many advantages, it’s also important to understand its challenges. Being aware of these helps you plan your project effectively.
Increased Development Complexity
A decoupled architecture involves more moving parts. Since front-end and back-end are separate, they must be maintained, deployed, and optimized individually.
This can increase initial development time and require developers skilled in both Drupal and front-end frameworks.
Limited Out-of-the-Box Preview
In traditional Drupal setups, editors can preview their content exactly as it appears on the website.
In a headless setup, since Drupal does not handle rendering, previews may not show the final layout. This can be resolved through custom preview systems or third-party tools, but it adds complexity.
SEO and Caching Considerations
Front-end frameworks often rely on client-side rendering, which can create challenges for SEO if not configured properly. Tools like Next.js and Gatsby handle this well through server-side rendering, but these must be integrated carefully.
Caching also requires attention since Drupal’s internal cache may not directly impact the front-end performance. You will need caching strategies both on Drupal’s side (using modules like Varnish or Redis) and on the front-end.
Higher Hosting and Maintenance Costs
Because you’re running two separate systems, hosting and maintenance costs can be slightly higher than with a traditional CMS. However, the improved performance and scalability often justify the investment.
Learning Curve
For teams new to API-driven development, there’s a learning curve. Editors, developers, and designers must adapt to a workflow that separates content creation from design presentation. Once mastered, though, the long-term benefits outweigh the initial challenges.
The Future of Headless Drupal
The demand for flexible, API-driven content management is growing rapidly, and Drupal is evolving right alongside it.
In fact, Drupal’s core development team has fully embraced the concept of headless architecture, ensuring that the platform remains one of the most capable CMS options for the next decade.
Recent versions of Drupal have improved API support, making it easier than ever to expose content to external applications.
The JSON:API module is now included in Drupal core by default, and ongoing work continues to refine GraphQL integrations, authentication methods, and performance optimizations.
In the near future, we can expect even stronger headless capabilities, such as:
- Native front-end integration tools to simplify setup for beginners.
- Enhanced editorial previews, allowing editors to visualize how content will look across different channels.
- More efficient caching and content delivery mechanisms, improving response times across multiple devices.
For agencies, developers, and enterprises, this means less time configuring and more time creating digital experiences.
Headless Drupal and the API-First Movement
Drupal’s evolution reflects a broader shift toward API-first development. Instead of building monolithic systems, businesses are now adopting composable architectures, where every part of a website or app communicates through APIs. Drupal’s strong API layer makes it an ideal foundation for this kind of modern setup.
This approach also aligns perfectly with the growing trend of microservices. Businesses no longer need one system to handle everything. Instead, they can connect specialized tools, such as eCommerce engines, analytics dashboards, and personalization platforms, directly to Drupal’s content hub.
The future of Headless Drupal lies in this kind of interconnected digital ecosystem, where content flows seamlessly across every user touchpoint, from websites and apps to wearables and smart assistants.
Emerging Trends with Headless Drupal
- AI-powered personalization – Integrating AI tools to deliver personalized content to users based on their behavior or preferences.
- Edge computing – Delivering Drupal-powered content closer to users for ultra-fast load times.
- Decoupled design systems – Standardizing front-end components so multiple teams can build interfaces that stay visually consistent.
- Content-as-a-Service (CaaS) – Turning Drupal into a full-scale content delivery platform that powers not just one website, but an entire digital ecosystem.
Drupal’s flexibility ensures it will continue adapting to these advancements, maintaining its reputation as a reliable choice for complex digital projects.
Partner with Brandout ADV for Smarter Web Solutions
At Brandout Adv, we build powerful, scalable, and future-ready web solutions that help businesses grow online.
Our expert team specializes in Drupal, headless CMS development, and modern front-end frameworks to create fast, secure, and user-focused digital experiences.
Whether you need a website, eCommerce platform, or an enterprise web application, Brandout Adv delivers innovation with precision, turning your digital goals into reality.
Conclusion
Drupal has always been known for its stability, scalability, and powerful content management capabilities. But in the era of digital transformation, those qualities alone are not enough. Businesses need agility, flexibility, and the ability to deliver content everywhere their audience is. This is where using Drupal as a Headless CMS truly shines.
By separating the content management layer from the presentation layer, organizations gain full creative control over their front-end experiences while maintaining Drupal’s editorial strength in the backend. The result is a fast, secure, and adaptable digital presence that can evolve with new technologies and user expectations.
For agencies, adopting a headless approach with Drupal means offering clients greater innovation potential. Websites can become faster and more engaging, mobile apps can be updated in real time, and content can flow seamlessly across every device, all powered by the same backend.
If your business plans to expand into multi-channel experiences, launch mobile apps, or simply future-proof your website, Drupal as a Headless CMS is one of the smartest investments you can make. It gives you a modern architecture that grows with your brand and a content engine that never limits your creativity.




