Enterprise integration software connects different IT systems, applications, and data sources within an organization into one unified system.
This connection removes barriers between departments, making business processes smoother and faster.
When systems share data easily, teams can make better decisions with less manual work.
This improves overall efficiency and helps the company respond quickly to changes.
Integration software supports businesses in staying competitive and prepared for future growth.
It is an essential tool for companies aiming to keep their operations well-coordinated and productive.
This article covers important aspects of enterprise integration software and how to implement it effectively.
What is Enterprise Integration Software?
Enterprise integration software connects different systems like ERP, CRM, databases, and cloud tools, allowing them to share data automatically.
It removes the need for manual data entry and helps systems communicate smoothly. The software follows different integration patterns.
Data integration keeps records consistent across platforms. Process integration makes daily tasks run automatically.
Application integration ensures systems communicate in real time. Each one supports faster, more accurate business operations.
Tools such as MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, and Microsoft BizTalk are commonly used. This software helps build a connected and efficient technology environment across the organization.
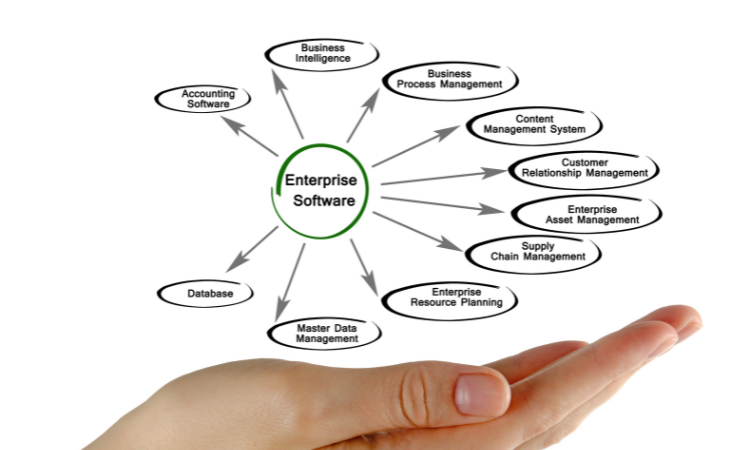
The following sections describe what enterprise integration software is, its key features, and the benefits it brings to organizations. Each part offers useful insights to help you understand and apply integration software in your company.
Features That Make Integration Software Effective
When evaluating integration software, considering the right enterprise integration software is a critical step.
A good platform should support smooth data flow, strong security, and future growth. Below are the most important features to consider before making a decision.
Connectivity
Strong connectivity means the software can easily link with many systems using ready-made connectors and APIs.
This allows faster setup and fewer technical challenges. It reduces the time required to connect ERP, CRM, or custom tools.
The more connectors a platform offers, the more flexible your setup becomes. Reliable connectivity also makes it easier to expand or replace systems later.
This ensures the integration can adapt as your needs change.
Scalability
Scalability allows the integration to grow with your business. As more systems are added, the platform should continue to perform well without delays.
It should handle larger volumes of data and support more users without slowing down. Businesses that expect to expand must plan for future demand.
Scalable platforms prevent the need for a full system upgrade later. They also help avoid performance issues during busy periods.
Security
Strong security protects sensitive business data as it moves between systems. Integration software should use encryption to keep information safe.
It should also include role-based access control so only the right people can see or edit data. Audit trails help track who did what and when.
These features reduce risks from both outside threats and internal mistakes. Secure platforms also support compliance with legal and industry standards.
Real-time Processing
Real-time processing ensures that updates happen immediately as data changes. This is useful in tasks like inventory tracking, order updates, or customer support.
It reduces delays and improves decision-making. When one system sends new information, others should receive it instantly.
This prevents errors caused by outdated records. Fast communication also supports smoother workflows across departments.

Monitoring and Analytics
Monitoring tools give insight into how the integration is performing. They can show delays, errors, and system health in one place.
Analytics help track trends and identify slow or broken connections. These tools support faster troubleshooting and ongoing improvements.
Good visibility allows IT teams to act before problems affect daily work. Over time, this helps maintain a stable and high-performing system.
Advantages of Connecting Systems with Integration Tools
Using enterprise integration software offers many advantages. It helps businesses work faster, reduce errors, and improve how they serve customers.
The following benefits show why this software is essential for organizations aiming to operate smoothly and adapt quickly.
Operational Efficiency
Enterprise integration software automates many routine tasks that would otherwise require manual work.
This reduces the chances of human error and frees employees to focus on more important duties.
For example, data entered once can automatically update all connected systems, saving time and effort.
Automation also speeds up processes like order handling or reporting. Overall, it helps organizations complete work faster and with fewer mistakes.
Data Consistency
When different systems do not share accurate information, errors and confusion can arise.
Integration software keeps data synchronized so all platforms have the same up-to-date information.
This consistency reduces conflicts and prevents duplicate or missing records. For example, customer details entered in one system will be immediately available in others.
Reliable data improves reporting and supports better decisions across the company.
Agility and Innovation
Integration software makes it simpler to add new applications or change workflows.
Businesses can respond quickly to new opportunities or challenges without rebuilding their entire system.
Flexible integration supports experimenting with new tools or automating additional processes.
This adaptability encourages innovation and helps organizations stay competitive. It also lowers costs and effort needed for technology updates.
Improved Customer Experience
Faster and more accurate service benefits customers directly. Integrated systems allow staff to access complete information quickly, enabling better support and faster responses.
For example, order status updates can be shared instantly, reducing delays and confusion.
Accurate data reduces errors in billing, shipping, and communications. This leads to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty over time.

Implementation Strategy
Implementing enterprise integration software requires careful planning and execution.
A step-by-step approach helps avoid common pitfalls and ensures the system works as expected.
The following stages guide organizations through a successful integration process.
Assess Needs and Objectives
Start by identifying which systems and processes need to be connected. Understanding the business goals is crucial, such as automating order processing or improving data reporting.
Clear objectives guide the entire project and help prioritize tasks. This step ensures the integration delivers real value and solves the most pressing problems.
It also aligns all teams on what success looks like.
Choose the Right Integration Platform
Selecting a suitable platform depends on your existing technology and future plans. Consider how well the software supports your current tools and if it fits the budget.
Also, check if the platform can grow as the business expands. Researching user reviews and technical support options is important.
The right choice will simplify setup and reduce long-term challenges.
Design Integration Architecture
Plan how data and processes will flow between systems. Mapping these flows clearly shows where information will be created, updated, or consumed.
Use standard protocols like REST or SOAP to promote compatibility. Well-designed architecture ensures systems communicate efficiently and securely.
This blueprint helps developers and IT teams understand the integration’s structure before building.
Data Mapping and Transformation
Data often exists in different formats or contains errors. Cleaning and normalizing this data makes it possible to move smoothly between systems.
Data mapping matches fields from one platform to another to avoid confusion. Transformation processes adjust the data format so each system can use it correctly.
This step prevents errors and maintains data quality across the network.
Testing and Validation
Before full deployment, test the integration thoroughly. Running pilot programs helps uncover errors, slow points, or missing data.
Users involved in testing can provide valuable feedback. Validation ensures the system meets the goals set in the first step.
This reduces surprises after launch and improves overall reliability.
Deployment and Monitoring
Deploy the integration gradually to reduce risks and allow adjustments. Monitor system performance closely during rollout to catch issues early.
Use tools to track data flows and alert teams to problems. Fix issues quickly to maintain smooth operation.
Continuous monitoring also helps identify opportunities for future improvements.

Trouble Areas in Integration Projects
Implementing enterprise integration software comes with its own set of difficulties.
Knowing these challenges in advance can help teams prepare better and avoid major disruptions.
Below are some of the most common issues organizations face during the process.
Complex Architecture
Many businesses rely on older systems that were not built to work with modern tools.
Connecting these legacy systems to newer platforms can become a major technical challenge.
Different formats, outdated protocols, and limited documentation often make integration harder.
Careful planning and specialized tools are needed to handle these complexities. Without proper attention, such systems may slow down the entire project.
Data Silos
Sometimes, departments store their data in separate systems that do not share information.
This lack of connection creates gaps and prevents smooth data flow. If data is poorly organized or inconsistent, integration tools struggle to sync it correctly.
These silos often lead to duplicate records and missed insights. Cleaning and standardizing data must happen before full integration begins.
Security Risks
When systems share data, protecting that information becomes more difficult. Without strong security practices, sensitive data may be exposed to outside security threats.
Unprotected channels or weak access controls increase the risk of breaches.
Regular security checks, strong encryption, and strict user roles are needed to guard the system. Ignoring these steps can lead to serious consequences.
High Initial Costs
Starting an integration project often requires a large investment. Licensing fees, new software, setup time, and staff training all add to the cost.
Smaller businesses may struggle to afford the upfront expenses. However, planning the budget carefully and choosing scalable tools can help manage these costs.
Over time, the benefits usually outweigh the early spending.
Best Practices for a Smooth Enterprise Integration Process
Every successful enterprise integration depends on smart planning and consistent execution.
Following best practices helps avoid costly mistakes and creates a system that works reliably over time.
These tips support smoother adoption and stronger results from your integration software.
Involve Stakeholders Early
Engage decision-makers, managers, and users right from the beginning. Their input helps shape a solution that fits actual needs, not just technical goals.
Early involvement also builds trust and reduces resistance during rollout. Stakeholders can identify gaps that others might overlook.
Their support often leads to better adoption and long-term success.
Prioritize Security
Protecting sensitive information is essential. Use strong identity management tools to control access to data.
Apply encryption so information stays safe while moving between systems. Perform regular checks to ensure compliance with laws and company rules.
Ignoring security can lead to serious financial and legal risks. A secure setup builds user confidence and trust.

Use Middleware When Appropriate
Middleware can simplify complex integrations by acting as a bridge between systems.
It handles tasks like message routing, data transformation, and protocol conversion.
This reduces the work required from developers and shortens delivery time.
Middleware can also improve flexibility, allowing easier changes in the future. Choose a reliable solution that matches your technical needs.
Plan for Scalability
Think beyond current needs. The software should support future system expansions and higher data volumes.
A scalable design prevents performance issues as the business grows. It also avoids the cost and hassle of major upgrades later.
Planning for growth from the start ensures long-term stability and better return on investment.
Provide Training and Documentation
People must know how to use the system correctly. Offer hands-on training sessions so users understand workflows and tools.
Well-written documentation helps new team members learn faster and reduces support requests.
Training also improves efficiency and minimizes user errors. Clear guides and ongoing support make the system easier to adopt.
Next Generation Features in Integration Software
Technology continues to change, and integration tools are evolving to keep pace.
Businesses that stay aware of these trends can make smarter decisions and prepare for what lies ahead.
Here are some key developments shaping the future of enterprise integration software.
AI-Powered Automation
Artificial intelligence is starting to play a bigger role in integration. It can help detect patterns, predict failures, and route data more efficiently.
AI reduces manual work by learning from past behavior and adjusting workflows automatically.
This makes systems smarter and more responsive. Over time, AI can help improve performance and lower operating costs.
Event-Driven Architecture (EDA)
Event-driven systems react instantly to changes, like a new customer order or payment.
Instead of waiting for scheduled updates, systems respond in real time as events happen.
This leads to faster processing and better coordination between departments. EDA improves accuracy and supports time-sensitive operations.
It also makes systems more flexible and responsive.
Low-Code Integration Tools
Low-code platforms allow users to create integrations with simple visual tools. This means even people without programming experience can build useful connections.
It speeds up development and reduces the load on technical teams. Low-code tools are helpful for quick projects and changing business needs.
More companies are choosing these tools to increase productivity.
Cloud-Native Integration
Cloud-based systems are now common in many businesses. Integration tools built specifically for the cloud work better with software like CRM, ERP, and finance platforms.
These tools can scale easily and support remote access. Cloud-native integration reduces hardware costs and simplifies maintenance.
It also supports faster updates and stronger system uptime.

Ready to Integrate Smarter with BrandOutAdv?
If your business needs seamless enterprise integration, BrandOutAdv delivers solutions through expert custom software development.
Our team builds software that connects your existing tools, improves workflows, and fits your exact requirements.
We do not rely on one-size-fits-all platforms; we create what works best for you. Let BrandOutAdv help you integrate smarter, faster, and with lasting results.
Final thoughts
Enterprise integration software helps connect systems, reduce errors, and improve business operations.
It supports smoother workflows, better data sharing, and faster decision-making.
A thoughtful approach starting with clear goals and ending with strong monitoring makes implementation more effective.
As technology changes, staying connected through reliable integration becomes even more important.
This software is not just a technical upgrade. It is a long-term tool for better performance and business growth.
Most asked questions:
How does enterprise application integration work?
Enterprise application integration connects different software systems so they can share data and work together smoothly.
It uses tools like APIs, middleware, and message queues to let systems send and receive information in real time.
This helps departments avoid duplicate data, speed up processes, and work from a single source of truth.
What is the best integration platform?
There is no single “best” integration platform. The right one depends on your business size, goals, and current systems.
Some popular and trusted options include MuleSoft, Dell Boomi, Microsoft BizTalk, and Apache Camel.
The best platform should support easy connections, strong security, and future growth.
Why are organizations trying to integrate their business processes?
Organizations want better speed, accuracy, and teamwork across departments.
Integration helps remove manual steps, avoids repeated data entry, and keeps all teams working with the same information.
This improves decision-making, lowers costs, and makes services faster and more reliable for customers.
What is an enterprise system with an example?
An enterprise system is software used by a business to manage key functions like finance, sales, human resources, or inventory.
For example, SAP ERP is an enterprise system that helps large companies handle accounting, supply chain operations, and employee records all in one platform.